How ChatGPT and Perplexity Use Website Content for AI Answers
How ChatGPT and Perplexity Use Website Content for AI Answers.
ChatGPT SEO feels opaque when AI assistants reference “the web” without showing how they’ve used your recruitment site or why competitors keep winning the citations. You see ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other assistants quoting generic articles while your niche sector pages, salary guides, and hiring explainers sit invisible in their answers.
For recruitment marketers, this creates a specific pressure: you must protect candidate and client pipelines inside AI channels you don’t fully control, with limited technical support and no time to parse long AI whitepapers. You need a small set of actions you can implement from your CMS, content plan, and robots.txt that increase AI citations without breaking compliance or exposing sensitive information.
Key takeaways
- ChatGPT SEO is the process of structuring recruitment website content so large language models can understand, trust, and reuse it in AI-generated answers, especially when browsing or search features run.
- Perplexity AI behaves as an answer engine that always retrieves live web content and attaches explicit citations, so concise, high-signal recruitment explanations have a real chance to win visibility.
- OpenAI and Perplexity crawlers respect robots.txt, which lets recruitment agencies decide which sections AI systems can train on or retrieve for live answers.
- Question-led sections, clear entities, and FAQ-style content make it easier for AI assistants to lift and attribute recruitment expertise from your site instead of defaulting to generic sources.
Does ChatGPT read websites?
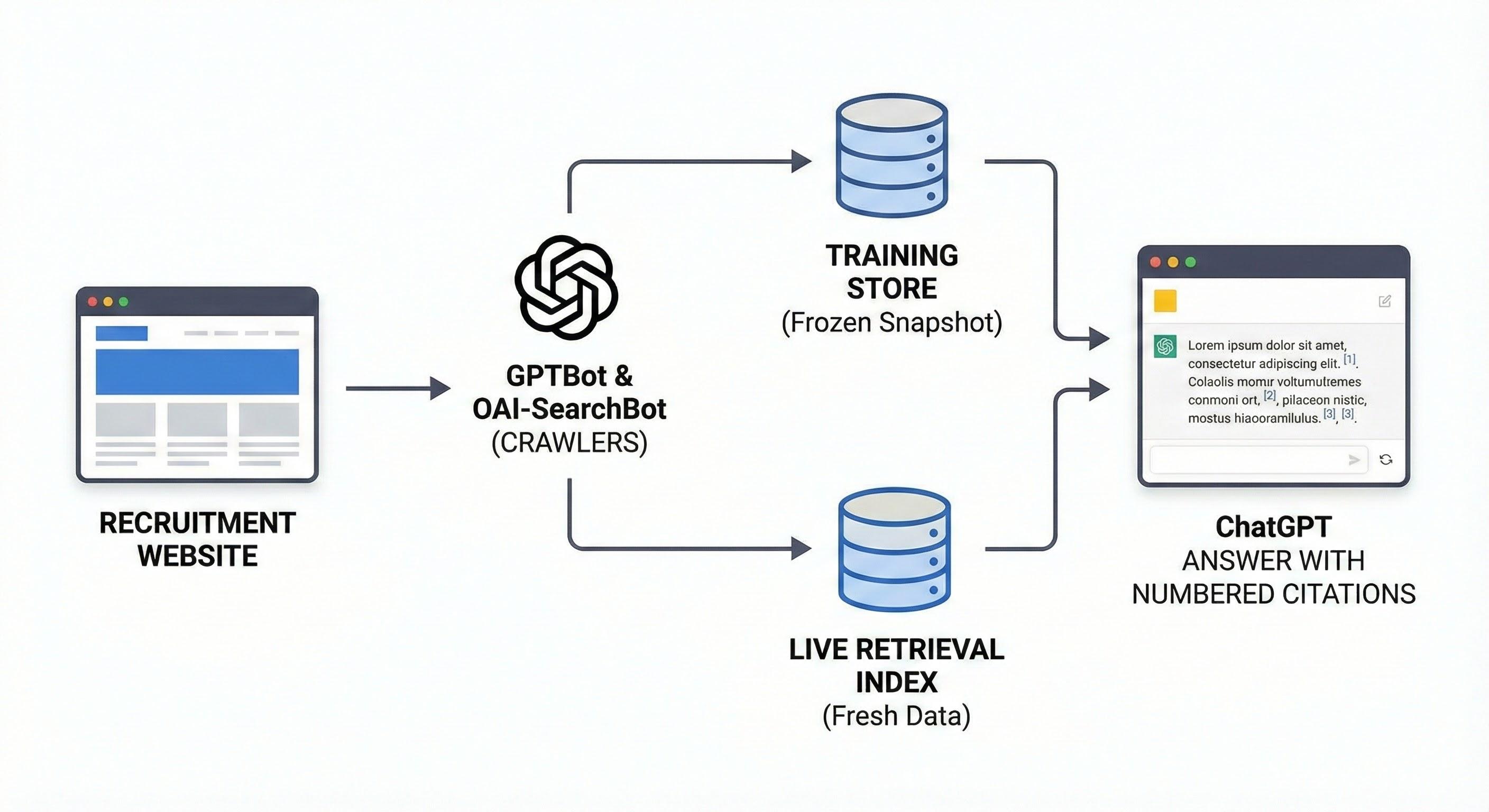
ChatGPT reads websites through a mix of pre-collected training data, dedicated crawlers (such as GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot), and live browsing or search features that pull current pages into the response context.
ChatGPT’s base model learns from historic datasets that include licensed sources and public web content collected before a specific cut-off date. When a user enables browsing or ChatGPT Search, the assistant sends the query to a search index, selects a small set of pages, and injects snippets of those pages into the prompt window, with numbered citations so users can see the original URLs.
For recruitment agencies, this means your content can influence ChatGPT answers as part of training and as a live, cited source, provided your robots.txt allows the relevant crawlers to access those paths.
How do AI crawlers access recruitment content?
Access depends on the user agents they use and the rules you’ve set in robots.txt. OpenAI publishes specific user agents for GPTBot (training) and OAI-SearchBot (search), and both declare that they respect robots.txt directives, including path-level allow and disallow rules.
When these crawlers hit your recruitment site, they read robots.txt first, then request approved URLs such as sector pages, guides, and salary content. In practice, log-file reviews show that GPTBot can generate thousands of hits on open domains, which confirms that AI systems already see and cache recruitment content unless you’ve explicitly blocked them.
You can let OAI-SearchBot read your public guides to support ChatGPT Search visibility while restricting GPTBot from training on sensitive areas if your legal team prefers a tighter stance.
What are the differences between training data and live retrieval?
The main differences are how fresh your content is in answers, how visible your URLs are, and how directly you can steer which queries you support.
- Training data acts like a frozen snapshot: the model learns general patterns about recruitment topics but doesn’t reference your live URL every time it generates a sentence.
- Live retrieval, such as ChatGPT’s browsing mode, fetches current pages, extracts short passages, and attaches citations directly to your site, so users can click from the answer to your page.
For recruitment marketers, this means you should treat training as background influence and design your highest-value sector and “how recruitment works” content for retrieval: clean headings, short answer paragraphs, and explicit entities that reflect how people search.
How does Perplexity get answers from websites?
Perplexity works by running every query through real-time web search, choosing relevant pages, extracting key passages, and generating a response covered with inline citations.
Perplexity positions itself as an “answer engine” that always draws on current web data rather than using only static training snapshots. When someone asks a recruitment question, Perplexity searches the web, scores candidate pages, and pulls short snippets that address the different parts of the query. It then composes a final answer and attaches numbered references or inline links, so users can see exactly which sites (including your recruitment site) provided each piece of information.
How does citation-based answer generation work in Perplexity?
Citation-based generation works by tying specific parts of the answer back to one or more live web pages that the system retrieved for the query.
Perplexity first builds a shortlist of relevant pages from web search, then identifies the sentences or paragraphs inside those pages that best match each part of the question. The assistant rephrases or combines those snippets into an answer and places citations next to statements so users can expand or open the source.
Recruitment pages that provide direct, context-rich explanations of topics like “IR35 for contractors,” “retained search fees,” or “graduate hiring timelines” tend to win more citations than generic homepages, because the snippets stand alone cleanly.
What trust and source evaluation signals matter for Perplexity?
Signals that matter include domain credibility proxies, topical focus, freshness, and alignment between page content and visible elements like title and headings.
Analyses of Perplexity outputs show that it prefers sites that consistently cover a topic, keep content up to date, and present clear, structured information. For recruitment agencies, that translates into:
- Giving each sector or role family a focused page instead of mixing multiple verticals on one generic services page.
- Keeping salary guides, process explainers, and compliance content updated so crawlers see current details.
- Matching titles and H1s to the queries you care about, such as “IT recruitment agency fees in London” or “How retained executive search works in healthcare.”
We often see Perplexity reward agencies that publish deep “how hiring works in [sector]” guides rather than relying on thin “about us” copy that says little about specific markets.
How do AI bots cite recruitment content?
Bots cite content by scanning pages for short, high-confidence passages that directly answer a question, then attaching visible references to those source pages in the final answer.
ChatGPT’s browsing features typically show numbered citations linked to a small set of retrieved sources, while Perplexity displays inline links or expandable source panels. These systems favour content that states facts clearly, names entities unambiguously (for example, sector, location, seniority), and avoids vague, heavily promotional language.
For recruitment marketers, AI attribution becomes much more likely when you treat each section and FAQ as a stand-alone answer that a bot could copy with minimal trimming.
How should recruiters structure content for attribution?
Recruiters should organise pages around question-first headings, direct answers, and entity-rich phrasing that mirrors how candidates and clients search.
A practical structure:
- Use H2 and H3 questions like “How does retained recruitment work for fintech roles?” or “What does a senior DevOps contractor earn in Manchester?”.
- Start each section with a one-sentence answer that mentions the key entities: sector, location, seniority, and contract type.
- Add 2-3 sentences of context that reflect real hiring steps, timeframes, or salary ranges where you’re allowed to discuss them.
In our experience, this structure makes it easier for ChatGPT and Perplexity to match a passage to a query, which increases the chance they’ll attribute your site on topics like hybrid working policy, contractor compliance, or local talent shortages.
What technical controls should recruiters use for AI access?
Controls include robots.txt rules, meta directives, and, where available, AI-specific opt-out conventions to manage which content AI systems crawl or reuse.
OpenAI’s documentation confirms that GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot respect robots.txt, and you can set separate directives for training and search. Other AI bots, including Perplexity’s crawler, identify themselves with user-agent strings that you can allow or block based on your policy.
For most recruitment agencies, a pragmatic setup is:
- Allow AI crawlers on public guides, sector pages, and generic resources you’re happy to see quoted.
- Disallow access to candidate portals, private job specifications, and content that could include personal or sensitive data.
- Document your AI policy so marketing, IT, and legal teams agree on what you’ve allowed and why.
How to optimise recruitment content for ChatGPT and Perplexity citations
Optimisation comes down to making your content easy to crawl, easy to interpret, and easy to quote for specific recruitment tasks.
Step 1: Confirm AI crawler access and policy
Audit server logs and analytics for GPTBot, OAI-SearchBot, and PerplexityBot, then check robots.txt to see what they can access today. Decide which paths you want AI to use for visibility and which paths you must protect for compliance, and update robots.txt accordingly.
Step 2: Rewrite priority recruitment pages around questions
Pick your highest-value niches, such as retained healthcare search or contract engineering in specific cities, and rebuild those pages with H2 and H3 questions that mirror real searches. Lead each section with a direct answer in one sentence, then add detail that reflects actual process, expectations, and outcomes instead of generic recruitment slogans.
Step 3: Make entities and definitions explicit
Name sectors, locations, role families, and contract types clearly in headings and opening sentences so AI systems don’t have to infer context. Add short glossary-style definitions for recruitment terms like “retained search,” “RPO,” “IR35,” and “LLM,” in plain language that assistants can quote word-for-word.
Step 4: Add structured data and clarify internal links
Implement Article, Organization, Service, and JobPosting schema so crawlers can distinguish guides, services, and job listings on your site. Link AI-focused content (for example, ChatGPT SEO guides) to sector and role pages, and link back from those pages to your guides, so assistants see a consistent authority cluster around each recruitment topic.
Step 5: Monitor AI citations and refine content
Regularly test high-intent recruitment queries in ChatGPT’s browsing modes and Perplexity, note when your domain appears, and capture the exact passages they quote. Tighten those passages for clarity, entity usage, and compliance, and apply the same patterns to adjacent pages that target similar sectors or locations.
FAQs
Does ChatGPT read websites?
ChatGPT reads websites using training data plus live browsing that relies on crawlers like GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot, controlled by robots.txt. When browsing is active, ChatGPT fetches a handful of pages, lifts short snippets, and adds numbered citations that link directly to those sources.
How does Perplexity get answers from recruitment sites?
Perplexity gets answers from recruitment sites by running real-time searches, selecting relevant pages, and extracting short passages for each query. Perplexity then composes a response and attaches inline citations, so users can see and click the recruitment websites behind each statement.
How do AI bots decide which sources to cite?
AI bots decide which sources to cite by scoring pages and passages for relevance, clarity, authority, and intent match. Focused topics, clean headings, and concise recruitment explanations usually beat generic, sales-heavy pages when assistants choose what to quote and reference.
What can recruiters change to appear in ChatGPT answers?
Recruiters can appear in ChatGPT answers by using question-led headings, explicit recruitment entities, and allowing OAI-SearchBot to access valuable guides and sector pages. This structure makes it easier for ChatGPT to parse sections, extract strong passages, and attach clickable citations.
Should recruitment sites block GPTBot and other AI crawlers?
Recruitment sites should block or allow GPTBot and other AI crawlers based on content sensitivity, legal advice, and their appetite for AI-driven visibility. A balanced approach lets crawlers access public guides and sector pages while excluding private candidate areas and high-risk content.
Author Bio
Dan Jones is a specialist AI visibility and recruitment SEO strategist with Kaizen SEO. Dan runs hands-on audits of crawler access, entity coverage, and AI citations for recruitment agencies, helping marketing teams turn complex ChatGPT SEO principles into clear content changes and robots.txt policies that protect inbound performance.
Book a consultation with Kaizen SEO to turn your recruitment site into AI-ready content that ChatGPT and Perplexity can safely crawl, interpret, and cite for high-intent candidate and client queries.
▸ Please note that for your privacy, no data from forms is stored on this website.